Question 1:
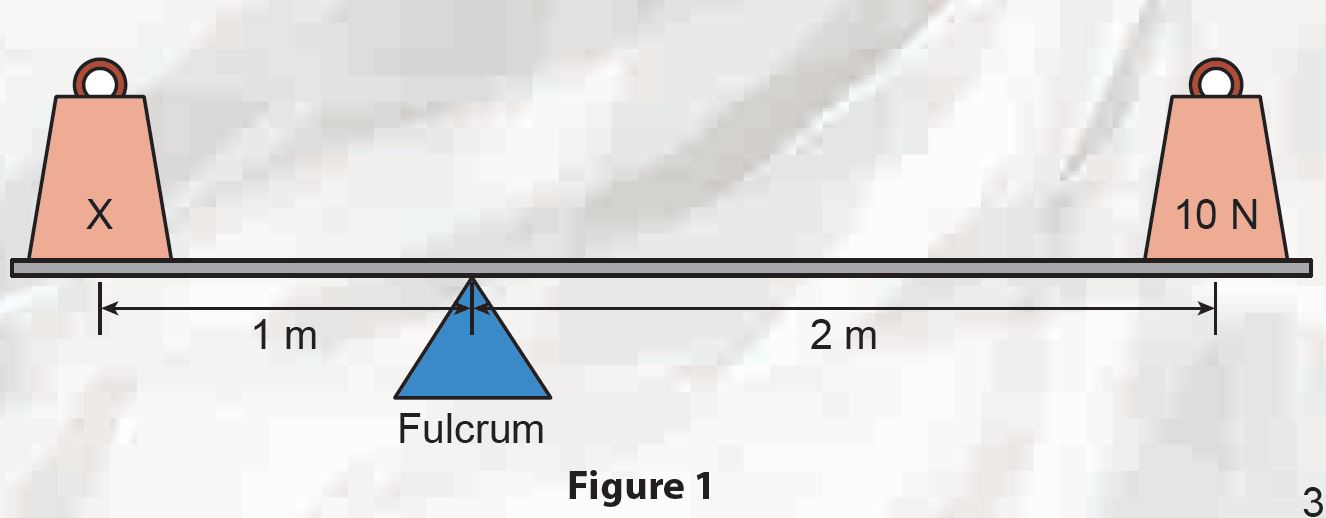
Figure 1 shows a lever system in equilibrium. Calculate the weight of X.
Answer:
20 N
Figure 1 shows a lever system in equilibrium. Calculate the weight of X.

Answer:
20 N
Question 2:
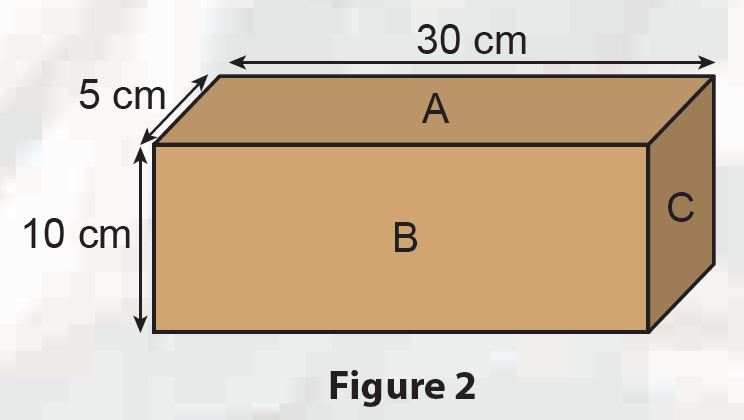
Figure 2 shows a cuboid with a weight of 5 N.
(a) Which surface will exert the greatest pressure?
(b) Calculate the pressure exerted by each surface.
Answer:
(a) Surface C
(b)
Pressure A = 0.03 N cm–2/ 333 N m–2
Pressure B = 0.0167 N cm–2/ 166.7 N m–2
Pressure C = 0.1 N cm–2/ 1 000 N m–2

Figure 2 shows a cuboid with a weight of 5 N.
(a) Which surface will exert the greatest pressure?
(b) Calculate the pressure exerted by each surface.
Answer:
(a) Surface C
(b)
Pressure A = 0.03 N cm–2/ 333 N m–2
Pressure B = 0.0167 N cm–2/ 166.7 N m–2
Pressure C = 0.1 N cm–2/ 1 000 N m–2
Question 3:
A balloon filled with helium gas will rise upwards when released and float at a certain height.
(a) Why does the balloon rise upwards?
(b) Explain the change in the size of the balloon as it rises higher.
(c) Show the forces acting on the balloon when it is floating with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
(a) The density of helium gas in the balloon is less than density of air
(b) The size of the balloon increases because air pressure decreases
A balloon filled with helium gas will rise upwards when released and float at a certain height.
(a) Why does the balloon rise upwards?
(b) Explain the change in the size of the balloon as it rises higher.
(c) Show the forces acting on the balloon when it is floating with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
(a) The density of helium gas in the balloon is less than density of air
(b) The size of the balloon increases because air pressure decreases