Activity 8.10:
Aim: To show the existence of atmospheric pressure in daily life.
Materials: Water and shredded paper
Apparatus: Plunger, Magdeburg hemisphere, straw, syringe, vacuum cleaner, beaker, drinking glass, rubber tube, tiles and basin
Instruction
Question 1:
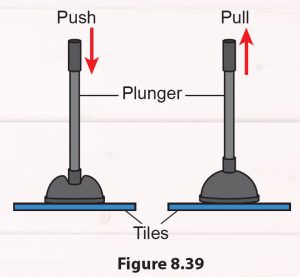
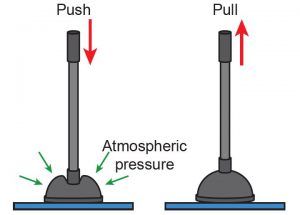
Wet the rim of a plunger with water. Press the plunger against a piece of tile so that air in the plunger is displaced (Figure 8.39). Try to pull the handle of the plunger. Can you detach the plunger from the tile? How is this situation related to atmospheric pressure?
Answer:
Aim: To show the existence of atmospheric pressure in daily life.
Materials: Water and shredded paper
Apparatus: Plunger, Magdeburg hemisphere, straw, syringe, vacuum cleaner, beaker, drinking glass, rubber tube, tiles and basin
Instruction
Question 1:
Wet the rim of a plunger with water. Press the plunger against a piece of tile so that air in the plunger is displaced (Figure 8.39). Try to pull the handle of the plunger. Can you detach the plunger from the tile? How is this situation related to atmospheric pressure?

Answer:

Question 2:
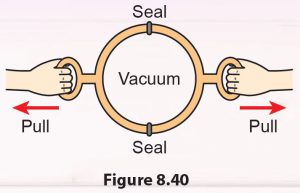
Attach two Magdeburg hemispheres together and turn the screws to remove the air inside. Try to pull and separate the two hemispheres (Figure 8.40). Can you do it? Explain this phenomenon.
Answer:
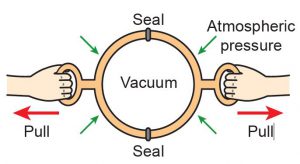
Attach two Magdeburg hemispheres together and turn the screws to remove the air inside. Try to pull and separate the two hemispheres (Figure 8.40). Can you do it? Explain this phenomenon.

Answer:

Question 3:
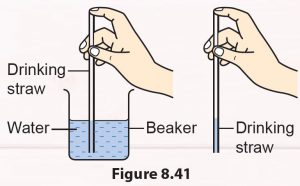
Fill a beaker with water and put in a drinking straw. Close the upper end of the straw (Figure 8.41). Lift up the straw. Observe what happens to the water in the straw. Explain your answer.
Answer:
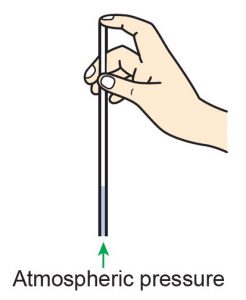
Fill a beaker with water and put in a drinking straw. Close the upper end of the straw (Figure 8.41). Lift up the straw. Observe what happens to the water in the straw. Explain your answer.

Answer:

Question 4:
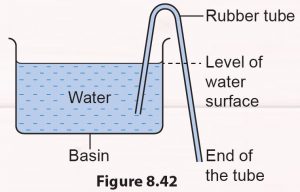
Arrange the apparatus as shown in Figure 8.42. Fill a rubber tube with water. Close both ends of the rubber tube. Then, place one end of the rubber tube in the water and the other end at a lower point outside the basin.
Observe what happens to the water in the basin. What happens if both ends of the tube are at the same level?
Answer:
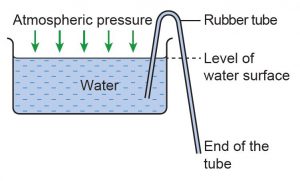
Arrange the apparatus as shown in Figure 8.42. Fill a rubber tube with water. Close both ends of the rubber tube. Then, place one end of the rubber tube in the water and the other end at a lower point outside the basin.
Observe what happens to the water in the basin. What happens if both ends of the tube are at the same level?

Answer:

Question 5:
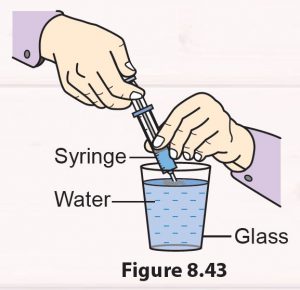
Insert a syringe into a glass of water (Figure 8.43). Pull the piston upwards. Observe what happens.
Answer:
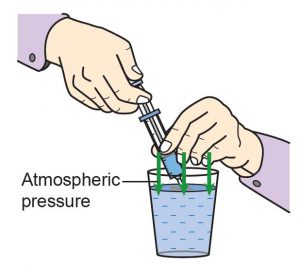
Insert a syringe into a glass of water (Figure 8.43). Pull the piston upwards. Observe what happens.

Answer:

Question 6:
Scatter shredded papers on the floor. Then, use a vacuum cleaner to suck all the shredded papers (Figure 8.44).
Observe what happens. How does the vacuum cleaner function?

Explain all the observations above using labelled figures to show the action of atmospheric pressure.
Answer:

Scatter shredded papers on the floor. Then, use a vacuum cleaner to suck all the shredded papers (Figure 8.44).
Observe what happens. How does the vacuum cleaner function?

Explain all the observations above using labelled figures to show the action of atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
