Activity 7.8:
Aim: To study current, voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit.
Apparatus: Dry cell holder, connecting wire, switch, bulb (1.5 V), dry cell, ammeter and voltmeter
Instruction
1. Set up a parallel circuit as shown in Figure 7.11 (a).
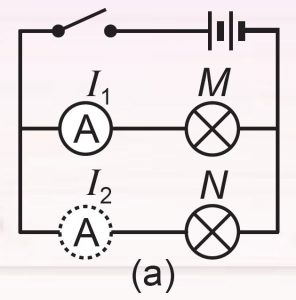
2. Turn on the switch and measure the current that flows through bulb M. Measure the current that flows through bulb N by changing the position of the ammeter.
3. Measure the electric current that flows through both the bulbs, M and N by setting up a circuit as shown in Figure 7.11 (b).
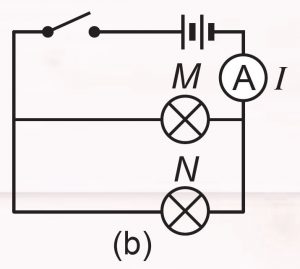
4. Fix the voltmeter across bulb M followed by bulb N as shown in Figure 7.11 (c) to measure the voltage across the bulbs.
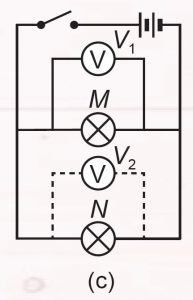
5. Fix the voltmeter as shown in Figure 7.11 (d) to measure the voltage across two bulbs.
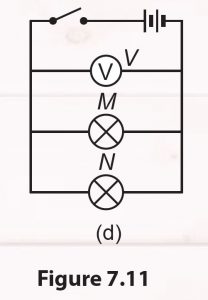
6. Calculate the resistance for each bulb separately and for both the bulbs using Ohm’s Law.
7. Record all the readings in a table.
Questions
1. Is the value of voltage different for bulb M and N?
2. List out the advantages and disadvantages of a parallel circuit.
Answer:
1. The voltages of bulb M and N are the same because the voltage in the parallel circuit is the same.
2.
The advantages of a parallel circuit
(a) Each device can be controlled by its own switch.
(b) The damage in one device does not interrupt the function of another device.
The disadvantage of a parallel circuit
The voltage in each device cannot be controlled.
Aim: To study current, voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit.
Apparatus: Dry cell holder, connecting wire, switch, bulb (1.5 V), dry cell, ammeter and voltmeter
Instruction
1. Set up a parallel circuit as shown in Figure 7.11 (a).

2. Turn on the switch and measure the current that flows through bulb M. Measure the current that flows through bulb N by changing the position of the ammeter.
3. Measure the electric current that flows through both the bulbs, M and N by setting up a circuit as shown in Figure 7.11 (b).

4. Fix the voltmeter across bulb M followed by bulb N as shown in Figure 7.11 (c) to measure the voltage across the bulbs.

5. Fix the voltmeter as shown in Figure 7.11 (d) to measure the voltage across two bulbs.

6. Calculate the resistance for each bulb separately and for both the bulbs using Ohm’s Law.
7. Record all the readings in a table.
Questions
1. Is the value of voltage different for bulb M and N?
2. List out the advantages and disadvantages of a parallel circuit.
Answer:
1. The voltages of bulb M and N are the same because the voltage in the parallel circuit is the same.
2.
The advantages of a parallel circuit
(a) Each device can be controlled by its own switch.
(b) The damage in one device does not interrupt the function of another device.
The disadvantage of a parallel circuit
The voltage in each device cannot be controlled.