Experiment 8.2:
Problem statement
What is the relationship between the angle of incidence, i and angle of refraction, r when light travels from a less dense medium to a more dense medium?
Hypothesis: The greater the angle of incidence, i, the bigger the angle of refraction, r.
Aim: To determine the relationship between angle of incidence, i and angle of refraction, r when light travels from a less dense medium (air) to a more dense medium (glass block)
Variables
Manipulated variable: The angle of incidence, i
Responding variable: The angle of refraction, r
Constant variable: The size of the slit, the shape of glass block
Materials and apparatus: Glass block, ray box with single slit plate, plastic ruler, power supply, white paper, protractor.
Procedure
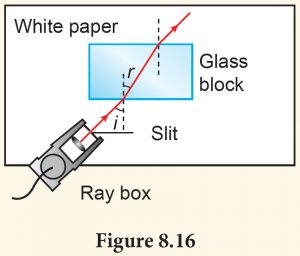
1. Carry out this experiment in the dark.
2. Place a glass block on a white paper and trace its outline.
3. Direct a single incident ray onto the block, mark its path and draw its incident ray with a ruler.
4. Mark the path of the ray emerging from the block and draw the ray with a ruler.
5. Remove the block, connect the entry and exit points to show the path of the ray inside the block.
6. Draw a normal line at the entry point.
7. Measure the angle of incidence, i and the angle of refraction, r using a protractor.
8. Repeat steps 3 to 7 for different angles of incidence.
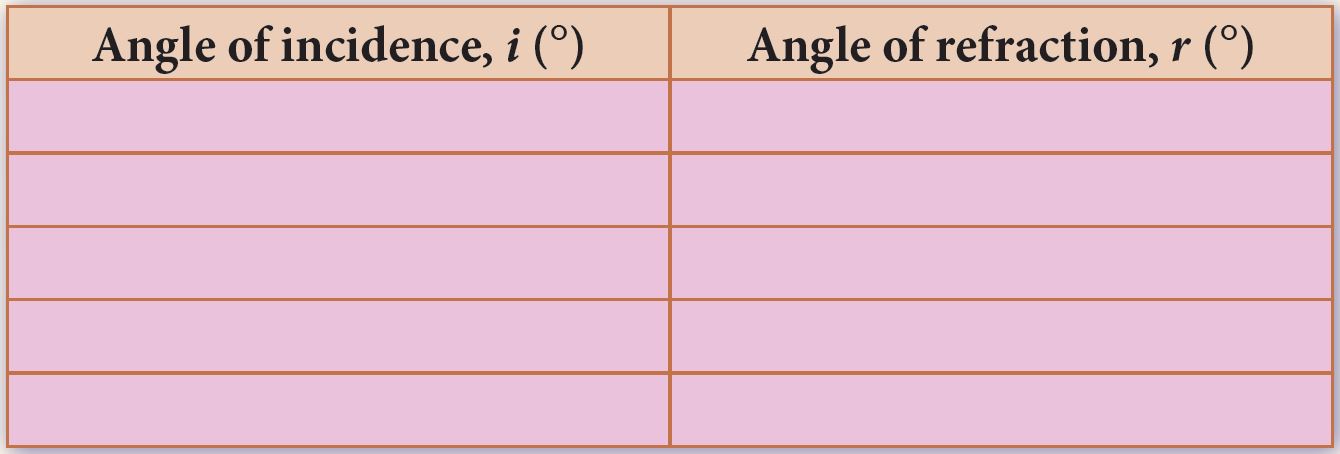
9. Record your results in a table.
Results
Discussion
1. Plot a graph of i against r.
2. Based on the graph of the angle of incidence, i against the angle of refraction, r, what is the relationship between the angle i with the angle r?
Conclusion
Can the hypothesis be accepted?
Question
What happen to the light ray when it travels from a
(a) less dense medium to a more dense medium?
(b) more dense medium to a less dense medium?
Answer:
1.
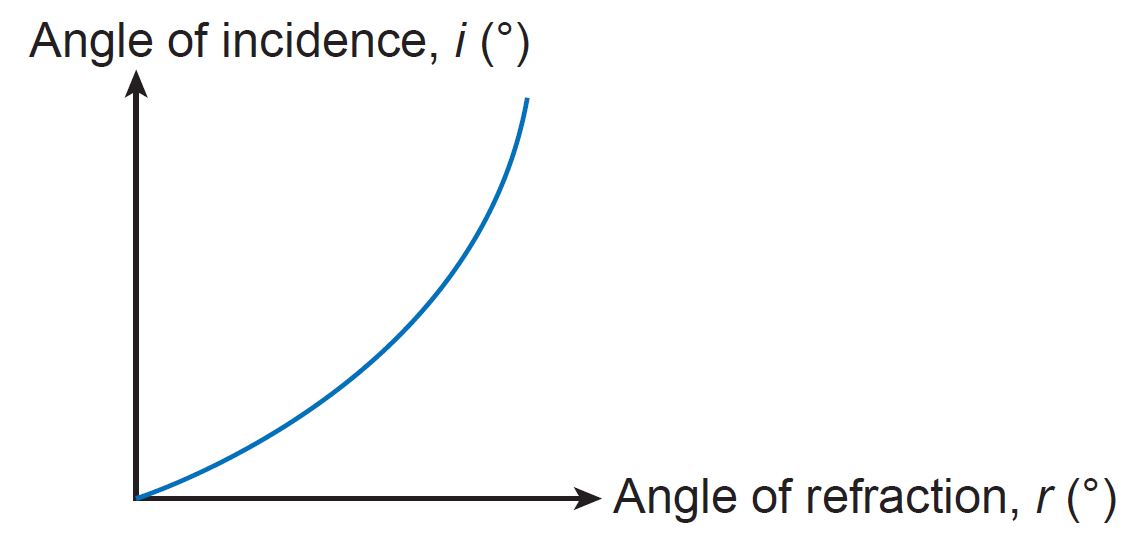
2. The bigger the angle of incidence, i, the bigger the angle of refraction, r.
Problem statement
What is the relationship between the angle of incidence, i and angle of refraction, r when light travels from a less dense medium to a more dense medium?
Hypothesis: The greater the angle of incidence, i, the bigger the angle of refraction, r.
Aim: To determine the relationship between angle of incidence, i and angle of refraction, r when light travels from a less dense medium (air) to a more dense medium (glass block)
Variables
Manipulated variable: The angle of incidence, i
Responding variable: The angle of refraction, r
Constant variable: The size of the slit, the shape of glass block
Materials and apparatus: Glass block, ray box with single slit plate, plastic ruler, power supply, white paper, protractor.
Procedure

1. Carry out this experiment in the dark.
2. Place a glass block on a white paper and trace its outline.
3. Direct a single incident ray onto the block, mark its path and draw its incident ray with a ruler.
4. Mark the path of the ray emerging from the block and draw the ray with a ruler.
5. Remove the block, connect the entry and exit points to show the path of the ray inside the block.
6. Draw a normal line at the entry point.
7. Measure the angle of incidence, i and the angle of refraction, r using a protractor.
8. Repeat steps 3 to 7 for different angles of incidence.
9. Record your results in a table.
Results

Discussion
1. Plot a graph of i against r.
2. Based on the graph of the angle of incidence, i against the angle of refraction, r, what is the relationship between the angle i with the angle r?
Conclusion
Can the hypothesis be accepted?
Question
What happen to the light ray when it travels from a
(a) less dense medium to a more dense medium?
(b) more dense medium to a less dense medium?
Answer:
1.

2. The bigger the angle of incidence, i, the bigger the angle of refraction, r.