Question 1:
State the subatomic particles.
Answer:
Proton, electron and neutron
State the subatomic particles.
Answer:
Proton, electron and neutron
Question 2:
Why is an atom neutral?
Answer:
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons. Thus, an atom is neutral.
Why is an atom neutral?
Answer:
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons. Thus, an atom is neutral.
Question 3:
What is meant by element and compound?
Answer:
An element is made of only one type of atom while a compound consists of two or more elements that are combined chemically.
What is meant by element and compound?
Answer:
An element is made of only one type of atom while a compound consists of two or more elements that are combined chemically.
Question 4:
Explain briefly the difference between atom and molecule.
Answer:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element while a molecule is a combination of two or more atoms.
Explain briefly the difference between atom and molecule.
Answer:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element while a molecule is a combination of two or more atoms.
Question 5:
How are the elements arranged in the Periodic Table?
Answer:
Elements are arranged according to their proton number.
How are the elements arranged in the Periodic Table?
Answer:
Elements are arranged according to their proton number.
Question 6:
Classify the elements below to metals and non-metals.
carbon, magnesium, iodine, chlorine, neon,
argon, aluminium, copper, iron, gold, mercury
Answer:
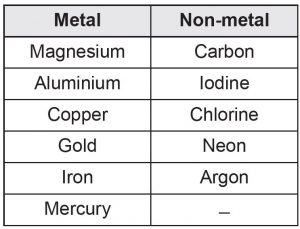
Classify the elements below to metals and non-metals.
carbon, magnesium, iodine, chlorine, neon,
argon, aluminium, copper, iron, gold, mercury
Answer:

Question 7:
You are given element X. What should you do to identify the element?
Answer:
Look at the physical properties of element X (appearance, ductility, malleability, electrical and heat conductivity and also melting point of the element)
You are given element X. What should you do to identify the element?
Answer:
Look at the physical properties of element X (appearance, ductility, malleability, electrical and heat conductivity and also melting point of the element)