Activity 8.1:
Aim: To investigate the presence of different types of forces.
Materials: Ball, wooden block, sandpaper and water
Apparatus: Spring, retort stand with clamp, 50 g weight, beaker and metre rule
(A)
Instruction
1. Throw a ball up in the air (Figure 8.1).
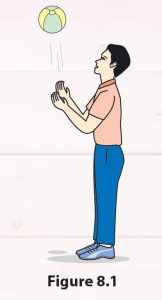
2. Observe whether the ball keeps going up or falls down.
(B)
Instruction
1. Place a wooden block on a table. Why does the wooden block remain in its position?
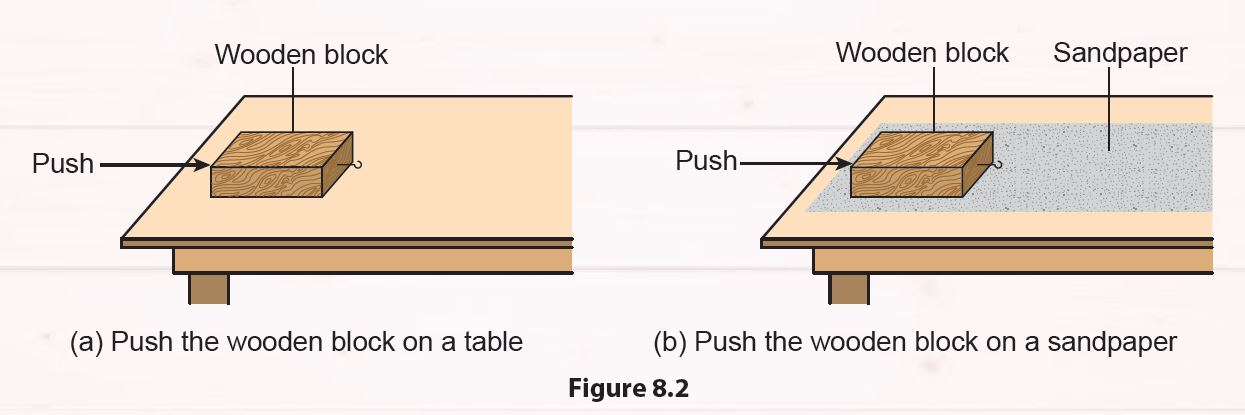
2. Then, push the wooden block (Figure 8.2 (a)).
3. Repeat step 2 by pushing the same wooden block on a sandpaper (Figure 8.2 (b)).
4. Compare the difficulty of pushing the wooden block on the table and on the sandpaper.
(C)
Instruction
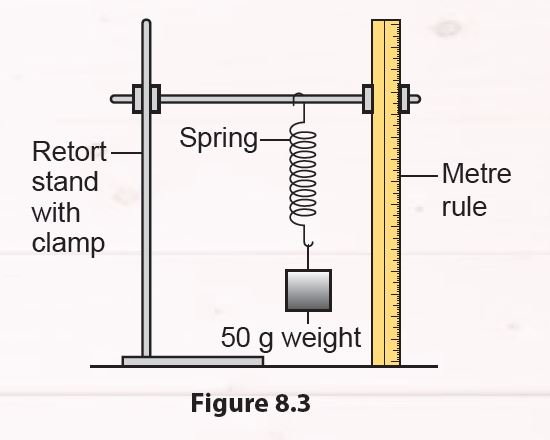
1. Hang a spring on a retort stand.
2. Hang a 50 g weight at the end of the spring (Figure 8.3).
3. Observe the change in the length of the spring.
4. Remove the weight and observe the change in the length of the spring.
(D)
Instruction
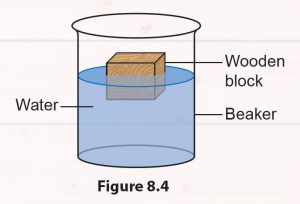
1. Place a wooden block on the surface of the water in a beaker (Figure 8.4).
2. Press the wooden block to the bottom of the beaker and release it.
3. Observe what happens to the wooden block.
Questions
1. Identify the forces involved in Activities A, B, C and D.
2. What is the type of force acting on stationary objects?
3. What is the type of force that resists the motion of objects?
Answer:
1.
Activity A: Gravitational force Activity B: Weight, normal force and frictional force
Activity C: Elastic force
Activity D: Buoyant force
2. Weight, normal force and frictional force
3. Frictional force
Aim: To investigate the presence of different types of forces.
Materials: Ball, wooden block, sandpaper and water
Apparatus: Spring, retort stand with clamp, 50 g weight, beaker and metre rule
(A)
Instruction
1. Throw a ball up in the air (Figure 8.1).

2. Observe whether the ball keeps going up or falls down.
(B)
Instruction
1. Place a wooden block on a table. Why does the wooden block remain in its position?
2. Then, push the wooden block (Figure 8.2 (a)).
3. Repeat step 2 by pushing the same wooden block on a sandpaper (Figure 8.2 (b)).
4. Compare the difficulty of pushing the wooden block on the table and on the sandpaper.

(C)
Instruction
1. Hang a spring on a retort stand.
2. Hang a 50 g weight at the end of the spring (Figure 8.3).
3. Observe the change in the length of the spring.
4. Remove the weight and observe the change in the length of the spring.

(D)
Instruction
1. Place a wooden block on the surface of the water in a beaker (Figure 8.4).
2. Press the wooden block to the bottom of the beaker and release it.
3. Observe what happens to the wooden block.

Questions
1. Identify the forces involved in Activities A, B, C and D.
2. What is the type of force acting on stationary objects?
3. What is the type of force that resists the motion of objects?
Answer:
1.
Activity A: Gravitational force Activity B: Weight, normal force and frictional force
Activity C: Elastic force
Activity D: Buoyant force
2. Weight, normal force and frictional force
3. Frictional force