Experiment 8.1:
Aim: To study the effect of density on the position of an object in water.
Problem statement: Will an object that is more dense than water submerge or float in water?
Hypothesis: An object that is more dense than water will submerge, while an object that is less dense than water will float.
Variables:
(a) Constant variable: Volume of blocks
(b) Manipulated variable: Density of blocks
(c) Responding variable: Position of blocks in water
Materials: Copper block, aluminium block, cork block and wooden block of the same size
Apparatus: Weighing scale, glass basin and metre rule
Procedure:
1. Weigh the mass of each block.
2. Calculate the volume of each block.
3. Calculate the density of each block using the following formula:
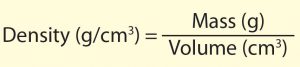
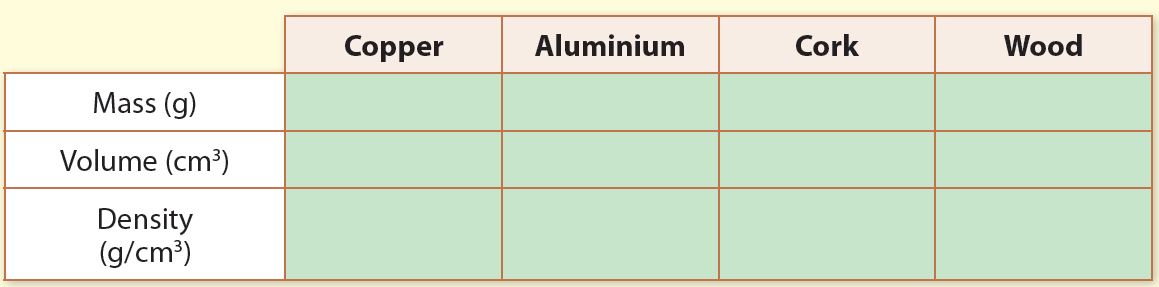
4. Record the mass, volume and density in the table below.
5. Put the four blocks into a glass basin filled with water. Observe the block that floats or submerges in water.
Conclusion:
Is the hypothesis accepted? Give your reasons.
Questions
1. Water has a density of 1.0 g cm–3. Which block is more dense than water?
2. State whether the block that is more dense than water floats or submerges in water.
Answer:
1. Copper, aluminium
2. The block which is more dense than water will submerge in water.
Aim: To study the effect of density on the position of an object in water.
Problem statement: Will an object that is more dense than water submerge or float in water?
Hypothesis: An object that is more dense than water will submerge, while an object that is less dense than water will float.
Variables:
(a) Constant variable: Volume of blocks
(b) Manipulated variable: Density of blocks
(c) Responding variable: Position of blocks in water
Materials: Copper block, aluminium block, cork block and wooden block of the same size

Apparatus: Weighing scale, glass basin and metre rule
Procedure:
1. Weigh the mass of each block.
2. Calculate the volume of each block.
3. Calculate the density of each block using the following formula:
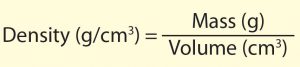
4. Record the mass, volume and density in the table below.

5. Put the four blocks into a glass basin filled with water. Observe the block that floats or submerges in water.
Conclusion:
Is the hypothesis accepted? Give your reasons.
Questions
1. Water has a density of 1.0 g cm–3. Which block is more dense than water?
2. State whether the block that is more dense than water floats or submerges in water.
Answer:
1. Copper, aluminium
2. The block which is more dense than water will submerge in water.