Question 1:
Name two strategies of human body defence system.
Answer:
Specific defence mechanism and nonspecific defence mechanism.
Name two strategies of human body defence system.
Answer:
Specific defence mechanism and nonspecific defence mechanism.
Question 2:
What is meant by antigen, antibody and immunity?
Answer:
An antigen is a foreign substance or a substance outside the body that stimulates the body’s immune system.
An antibody is a protein produced by white blood cells into the bloodstream in response to antigen.
Immunity is the ability of the body to fight against pathogens when the body is infected with pathogens.
What is meant by antigen, antibody and immunity?
Answer:
An antigen is a foreign substance or a substance outside the body that stimulates the body’s immune system.
An antibody is a protein produced by white blood cells into the bloodstream in response to antigen.
Immunity is the ability of the body to fight against pathogens when the body is infected with pathogens.
Question 3:
The graphs below show two types of immunity, P and Q.
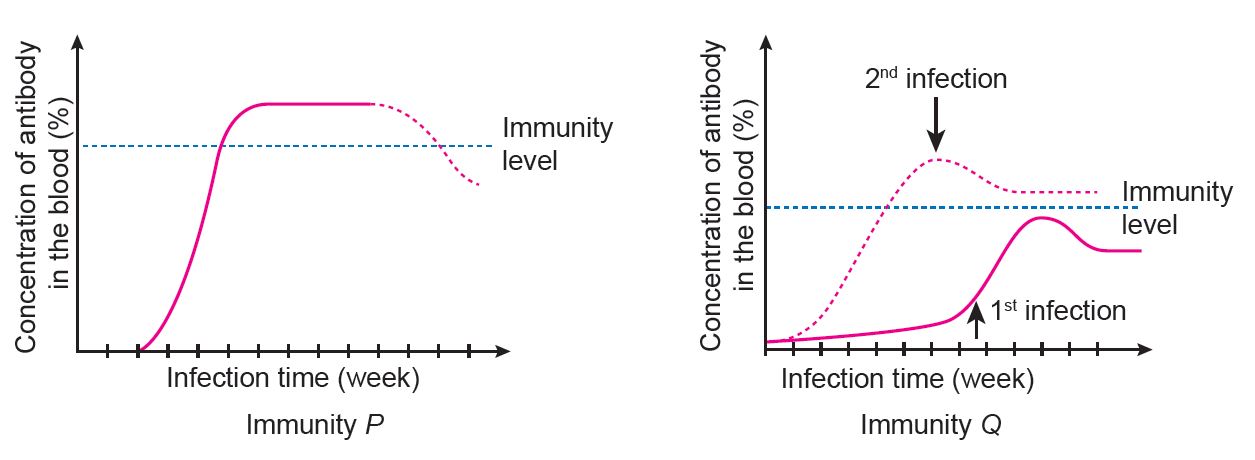
(a) Name immunity P and immunity Q.
(b) Explain the similarities and differences between immunity P and immunity Q.
(c) In your opinion, which immunity is better? Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
P: Passive natural immunity
Q: Active natural immunity
(b)
Similarity: Both immunities are obtained naturally without external help.
Difference: Immunity P is obtained when the body receives antibodies from breast milk or from the mother’s blood that flows across the placenta, whereas immunity Q occurs when antibodies are produced in an individual who has recovered from a disease.
(c)
Immunity Q is better because the concentration of antibody in the blood remains above the immunity level, whereas for immunity P, the concentration of antibody in the blood drops below the immunity level after a certain period.
The graphs below show two types of immunity, P and Q.

(a) Name immunity P and immunity Q.
(b) Explain the similarities and differences between immunity P and immunity Q.
(c) In your opinion, which immunity is better? Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
P: Passive natural immunity
Q: Active natural immunity
(b)
Similarity: Both immunities are obtained naturally without external help.
Difference: Immunity P is obtained when the body receives antibodies from breast milk or from the mother’s blood that flows across the placenta, whereas immunity Q occurs when antibodies are produced in an individual who has recovered from a disease.
(c)
Immunity Q is better because the concentration of antibody in the blood remains above the immunity level, whereas for immunity P, the concentration of antibody in the blood drops below the immunity level after a certain period.
Question 4:
Suggest two practices that weaken the immune system of a person.
Answer:
Smoking, undergoing unnecessary surgeries, eating imbalanced diet.
(Any other answers are accepted)
Suggest two practices that weaken the immune system of a person.
Answer:
Smoking, undergoing unnecessary surgeries, eating imbalanced diet.
(Any other answers are accepted)
Question 5:
Explain the reason why immunisation should be given to babies and children.
Answer:
Infectious diseases are the main cause of defect and death among babies and children. Immunisation is important because it can stimulate the baby to produce antibodies to fight against pathogens. Babies and children will be safe from infectious diseases and complications.
Explain the reason why immunisation should be given to babies and children.
Answer:
Infectious diseases are the main cause of defect and death among babies and children. Immunisation is important because it can stimulate the baby to produce antibodies to fight against pathogens. Babies and children will be safe from infectious diseases and complications.